Warehouse Racking Inspection Consultancy
We determine the appropriate standard to follow based on customer requirements. Our inspectors conduct comprehensive walkthrough of your facility, carefully assessing your racking systems for compliance.
They gatheron-site information, capture photos, and document any deficiencies, damage, or missing components. Our pallet rack inspection services are designed to be non-disruptive to your daily operations.
Following the inspection, we provide a detailed report with recommendations. Regardless of your industry, the type of pallet racks you use, or the extent of damage in your warehouse, we have the expertise and solutions to help you diagnose, report, and resolve deficiencies.
Under the WSH Act 2006, every workplace occupier must take reasonable measures to ensure that the workplace,access/egress points, and any machinery, equipment, or substances on the premises are safe and free from healthrisks for everyone, whether or not they are employees.
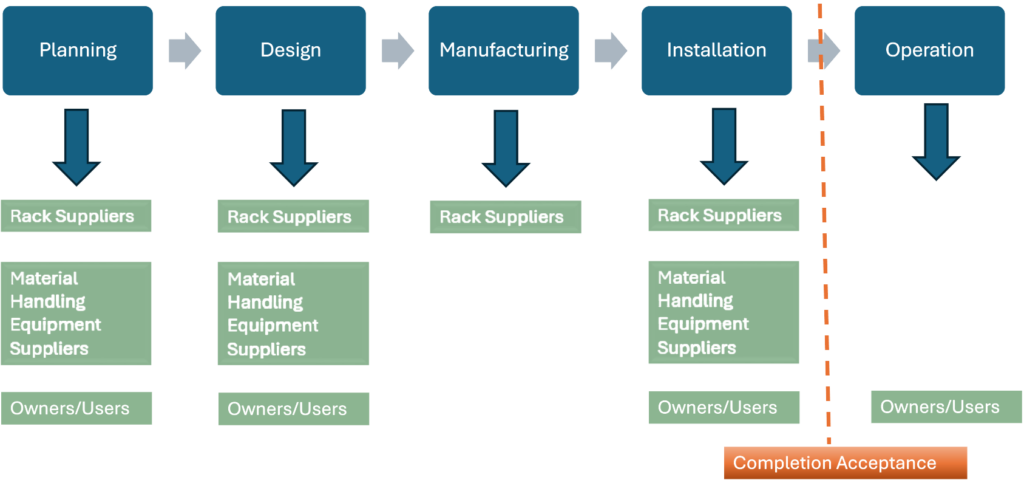
Warehouse racks must comply with relevant standards and specifications throughout their entire lifecycle,including planning, design, manufacturing, installation, operation, and use. Most companies in the industry adhereto European EN (FEM) standards, British SEMA standards, Australian AS4084 standards, and American RMI standards.
Common issues such as planning errors (e.g., inadequate safety clearance), design flaws (e.g., improper materialselection), structural displacement over time (e.g., out-of-tolerance verticality), component damage, loosefasteners, and protection failures can lead to significant risks. These hazards can be effectively mitigated by implementing a three-level inspection system and conducting annual professional inspections. This proactive approach is essential for minimizing safety risks and preventing costly losses.
Overloading occurs when the weight limit of a racking system is exceeded, which can lead to the rack tipping over or failing due to excessive weight.
Improper installation can cause instability if the racking system is not correctly anchored, leveled, or aligned, making it prone to tipping or collapsing.
Damaged racking components such as bent beams, uprights, or connectors weaken the structure, leading to instability and a higher risk of failure.
Poor maintenance contributes to instability, as the lack of regular inspections and repairs can cause unnoticed wear and tear, compromising the rack’s strength.
Improper handling of loads by forklifts or other equipment can shift the racks or place loads incorrectly, which may cause the racks to become unstable or collapse.
Environmental factors, such as changes in temperature, humidity, or seismic activity, can affect the stability of racks if the system is not designed to withstand such conditions.
1. Summary of Inspection Procedures and Field Observations
Our inspector will conduct a thorough on-site assessment using industry-standard inspection techniques and tools. This section of the report will outline the specific procedures followed, such as visual inspections, functional testing, or diagnostic evaluations. Additionally, it will provide a detailed account of observations made during the inspection, highlighting any irregularities, potential risks, or areas requiring further attention.
2. Expert Recommendations on Addressing Identified Issues
Based on the findings, our inspector will provide well-informed, practical recommendations for addressing any detected deficiencies or risks. These recommendations will be tailored to ensure compliance with relevant safety regulations and best practices. They may include suggested maintenance measures, necessary repairs, or system upgrades to enhance efficiency and longevity. Each recommendation will be accompanied by a rationale to help stakeholders make informed decisions.
3. Location Plan of the Inspected Systems with Supporting Photos
To enhance clarity and provide a visual reference, the report will include a detailed location plan pinpointing the inspected systems. High-resolution photos will accompany the descriptions to illustrate the current condition, highlight problem areas, and serve as a visual record for future reference. This documentation helps in tracking system conditions over time and aids in effective decision-making.
4. Repair Proposal, if Requested
If the client requests a repair proposal, our team will provide a comprehensive plan detailing the scope of work, estimated costs, and projected timelines for completing the necessary repairs. This proposal will include an itemized list of required materials, labor considerations, and any additional measures needed to restore the inspected systems to optimal working condition. Where applicable, alternative solutions may be presented to suit different budgetary or operational needs.